The Future of Healthcare on Blockchain
22 July 2025Healthcare systems handle a constant flow of information, from patient histories and lab results to prescriptions and treatment records typically stored in centralized databases that connect departments and support care coordination. However, these systems are vulnerable to delays during updates or outages, disrupting services in a 24/7 environment. Data sharing between hospitals is often slow and complicated, limiting timely access to critical information.
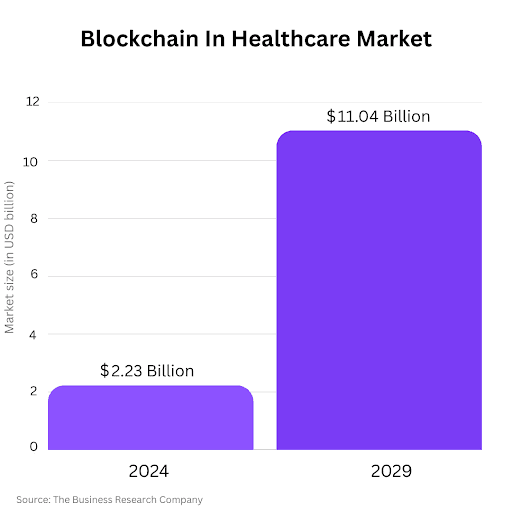
Blockchain is emerging as a foundational technology to address these challenges. Its decentralized, tamper-proof architecture helps eliminate data silos, enhance trust, and strengthen security. The blockchain in the healthcare market is projected to grow from $2.23 billion in 2024 to $11.04 billion by 2029, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38%. This growth is driven by needs like fraud prevention, secure data interoperability, patient empowerment, and immutable medical record keeping.
The Daily Struggles Inside Healthcare’s Walls
Despite rapid digital advancements, healthcare systems today still face deeply rooted challenges that affect both providers and patients. These issues lead to delays, errors, and inefficiencies that ultimately impact patient care.

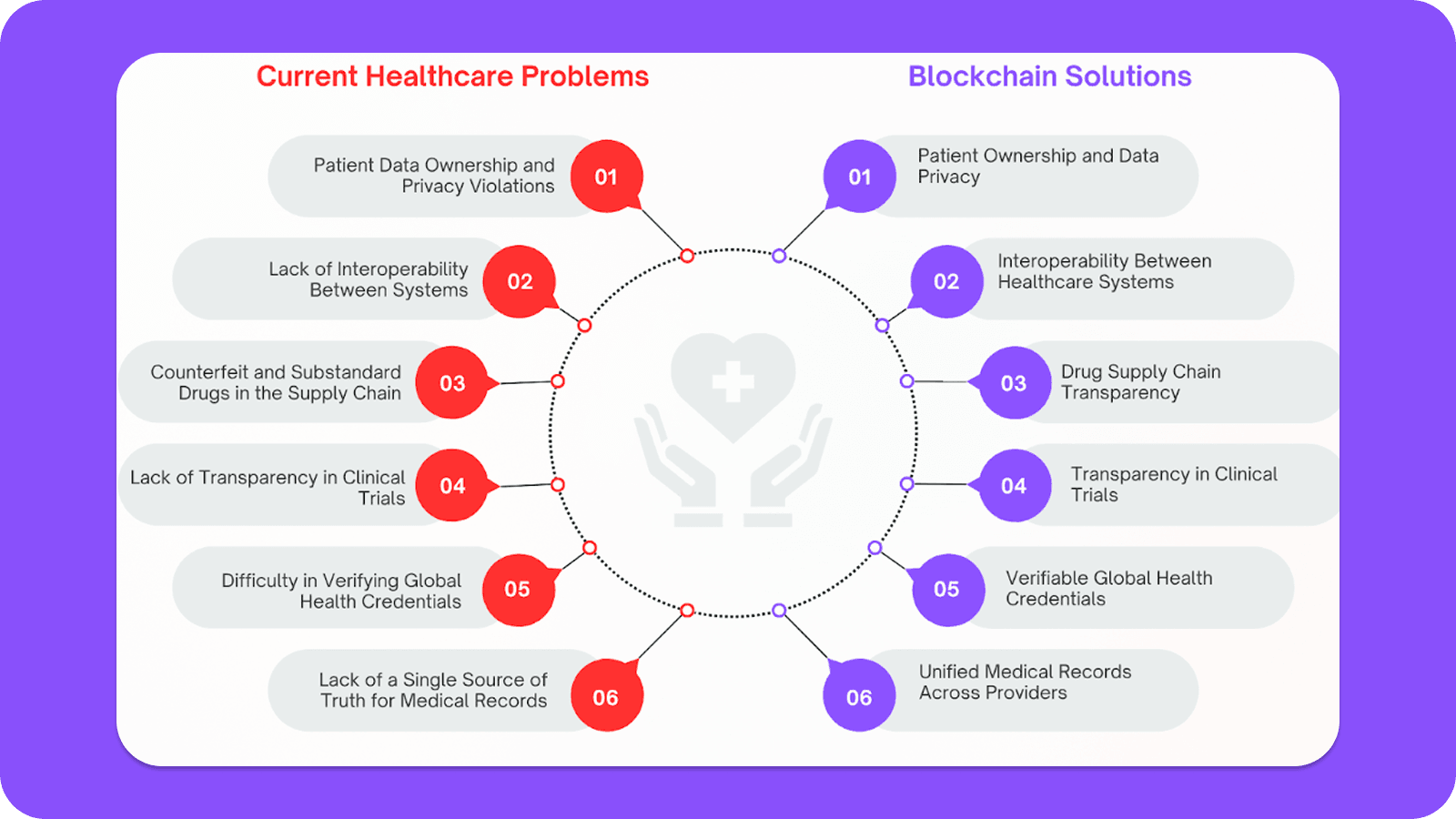
1. Patient Data Ownership and Privacy Violations
In today’s systems, patients rarely have full control over their health data. Medical records are typically managed by hospitals, insurers, or clinics, requiring patients to request access and navigate slow administrative processes. This centralized model not only limits transparency but also makes systems highly susceptible to data leaks. Healthcare data is extremely valuable on the black market, and frequent breaches caused by weak security or poor oversight expose sensitive personal, financial, and medical information. These incidents not only lead to identity fraud and institutional damage but also erode the trust patients place in medical centers and third-party data handlers, who are expected to securely manage and protect their private health data.
2. Lack of Interoperability Between Systems
Most healthcare providers use incompatible electronic health record (EHR) systems, creating silos that prevent seamless data exchange. As a result, patients receiving care from multiple sources often have fragmented records, making it hard to coordinate treatment. Providers may miss crucial information like allergies or test results, leading to duplicate procedures, delays, or even harmful errors, ultimately undermining the quality and efficiency of care.
3. Counterfeit and Substandard Drugs in the Supply Chain
The pharmaceutical supply chain involves numerous players across regions, making it difficult to track a drug’s journey from production to consumption. This lack of visibility allows counterfeit or substandard drugs to enter the system undetected. Such drugs can be ineffective or dangerous, causing serious health issues or death. When adverse events occur, tracing the source of contamination is challenging, hindering swift regulatory response and damaging public trust. The issue is further complicated by varying regulatory standards across different regions and countries, which create inconsistencies in oversight and enforcement throughout the supply chain.
4. Lack of Transparency in Clinical Trials
Clinical trials often suffer from selective reporting and limited access to raw data. Companies may withhold negative results or change trial parameters mid-study, which compromises scientific integrity. This practice misleads regulators and doctors, sometimes leading to the approval of unsafe or ineffective treatments. It also wastes research funding and raises ethical concerns, especially when participants risk their health without assurance that outcomes will be transparently reported.
5. Difficulty in Verifying Global Health Credentials
During global health crises like pandemics, verifying health credentials such as vaccination records or COVID-19 test results is essential for travel, work, and access to public spaces. However, there’s no standardized system for this. Most records are issued in formats like paper slips or emails, which can be easily lost or forged. As a result, authorities and organizations struggle to confirm the authenticity of these credentials in real time. This creates delays, increases fraud risk, and makes global health efforts less effective.
6. No Single Source of Truth for Medical Records
A patient’s health history is often fragmented across different hospitals, clinics, and specialists. There’s no single, unified record that aggregates all medical data over time. This makes it difficult to get a full picture of a patient’s condition. Without a central source of truth, healthcare professionals may rely on outdated or incomplete information, leading to misdiagnoses or dangerous drug interactions. It also prevents data-driven care, long-term disease management, and meaningful healthcare research.
A New Path Forward: How Blockchain Reimagines Healthcare
In the face of the serious challenges facing healthcare today, blockchain offers a fresh, game-changing solution. It completely reimagines how healthcare systems can work by providing a way to solve many of the problems we just discussed.
1. Patient Ownership and Data Privacy
In traditional healthcare systems, patients have little control over who accesses their medical records and how their data is stored. Blockchain changes this by giving patients direct ownership of their health data through decentralized identity systems. Each patient’s medical history is stored on a secure, encrypted ledger that only they can grant access to, using private keys. This eliminates unauthorized data sharing, reduces risks of data breaches, and ensures that patients can choose exactly which doctors or institutions see their information, empowering them with real privacy and control. Zero-knowledge (ZK) proofs serve as a backbone of this solution—allowing data to be anonymously stored in the healthcare database, with only the patient or trusted authorities able to reveal and link it to the individual when necessary.
2. Interoperability Between Healthcare Systems
Hospitals and clinics often use different software systems that don’t communicate well with each other, making it hard to share patient information across institutions. This lack of interoperability leads to duplicate tests, treatment delays, and fragmented care. Blockchain offers a standardized and decentralized way to record and access data, making it easier for healthcare providers, no matter the platform they use, to securely exchange information. Smart contracts and permissioned access ensure that data is shared only with trusted parties, enabling real-time collaboration across different systems without compromising security. Building on the same zero-knowledge (ZK) proof foundation as patient-owned data, healthcare systems can access anonymized records without revealing sensitive personal information—ensuring interoperability while preserving patient privacy.
3. Drug Supply Chain Transparency
Counterfeit drugs are a serious global issue, especially in developing countries. Blockchain can help track each drug from manufacturing to distribution in an immutable, transparent ledger. Every participant such as manufacturer, wholesaler, and pharmacy logs transactions on the blockchain, which means any attempt to tamper with the supply chain becomes instantly visible. This allows authorities and consumers to verify the authenticity of a drug by scanning a code that traces its complete history, significantly reducing the risk of fake medicines reaching patients. Moreover, in a global pharmaceutical market with varying regulatory requirements across regions, blockchain-enabled supply chains offer greater control and compliance by ensuring traceability and standardization across jurisdictions.
4. Transparency in Clinical Trials
Clinical trial results are often delayed, selectively published, or even manipulated, which undermines public trust and scientific integrity. Blockchain addresses this by making trial protocols, data, and outcomes tamper-proof and timestamped. Researchers can register a study, log every phase of the trial, and publish results on a public or consortium blockchain. This ensures transparency and accountability throughout the trial process, making it easier for regulators, peers, and the public to verify the validity and completeness of the data.
5. Verifiable Global Health Credentials
In a post-pandemic world, proving vaccination status or health history for travel, work, or events has become common. However, paper-based records or digital PDFs can be easily forged. Blockchain enables verifiable digital health credentials that are cryptographically signed and globally accessible. Whether it’s a COVID vaccination, yellow fever certificate, or chronic illness history, these credentials can be stored on a blockchain and verified in seconds without exposing sensitive details, making them ideal for global interoperability.
6. Unified Medical Records Across Providers
One of the biggest frustrations patients face is repeating their medical history every time they visit a new doctor. With blockchain, a patient’s complete medical history, prescriptions, diagnoses, test results can be recorded in a unified, tamper-proof record that can be accessed by any authorized provider, regardless of their hospital or clinic network. This ensures continuity of care, reduces unnecessary procedures, and allows for more accurate diagnosis and treatment, especially in emergencies where fast access to reliable medical data is critical.
Why Blockchain Makes Sense for Healthcare Today
As healthcare organizations embrace blockchain, the results go far beyond technical upgrades. They unlock real-world improvements that touch every corner of the system. Here’s how blockchain could finally turn today’s healthcare struggles into tomorrow’s success :
When a healthcare business migrates appropriate processes to blockchain, it can realize significant gains:
1. Cost reduction: By automating processes and eliminating middlemen, blockchain cuts administrative overhead. For example, replacing legacy billing systems with blockchain-enabled billing can reduce manual hours and errors. As one industry guide notes, blockchain “can be used as a tool to influence” major expenditures, from logistics to patient accounting. Automating claims and inventory tracking slashes labor costs and late-payment penalties.
2. Faster operations: Real-time blockchain transactions remove bottlenecks. Payments, claims, and transfers of records happen instantly (with smart contracts) rather than through slow batch processes.
In the past, blockchain was criticized for being too slow or expensive for large-scale healthcare operations. But Layer 2 technologies and rollups are changing that. These innovations allow thousands of transactions such as insurance claims, pharmacy updates, or record transfers to be processed in seconds instead of hours, with lower costs. By bundling transactions before sending them to the main blockchain, healthcare providers can maintain security without sacrificing speed.
3. Better patient trust and experience: Immutable audit trails and encrypted data give patients confidence that their records are secure and accurate. Patients can potentially access and control their own health data via a blockchain portal, improving engagement. In trials of blockchain for clinical studies or telemedicine, patients report higher trust knowing their consent and data use are transparently recorded. Zero-knowledge (ZK) proofs further enhance this trust by allowing verification and usage of sensitive data without exposing the underlying personal information, ensuring privacy is preserved even during data exchange or validation.
4. Regulatory compliance and auditability: Blockchains inherently log every transaction, which simplifies audits for HIPAA, the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA), GDPR, etc. Instead of patching together logs from disparate systems, an organization can query the blockchain to prove that access controls and data handling rules were followed. This reduces risk of fines and streamlines regulatory reporting.
5. Robust security: Finally, blockchain’s encryption and decentralization directly strengthen data security. By design, “blockchain’s ability to keep an incorruptible, decentralized and transparent log of all patient data makes it ideal for security applications”. Protecting patient data also preserves reputation and avoids the huge costs of breaches.
Blockchain Solutions Driving Healthcare Innovation
Several pioneering healthcare players are proving blockchain’s potential beyond theory:
1. BurstIQ – Secure Data Exchange & Personalized Health
BurstIQ’s LifeGraph Platform enables ethical, secure sharing of health data by connecting fragmented medical records into unified, privacy-respecting data ecosystems. Patients retain full control over their data, supporting personalized care, precision medicine, and AI-driven insights—all while staying compliant with HIPAA and GDPR.
2. MediLedger – Securing Pharma Supply Chains
Developed by Chronicled, MediLedger uses blockchain to verify drug authenticity and streamline transactions across pharma manufacturers, distributors, and health systems. It ensures compliance with the U.S. DSCSA, prevents counterfeit drugs, and enables secure, automated data sharing throughout the supply chain—boosting transparency and patient safety.
3. Guardtime – Blockchain for Health Record Security
Estonia-based Guardtime uses advanced hash-based cryptography and blockchain technology to secure sensitive health data. With deployments across Europe, Asia, and the U.S., Guardtime has enabled tamper-proof medical records and verifiable vaccine credentials, ensuring integrity and trust in public health systems. Its deep focus on research and cryptographic innovation makes it a global leader in healthcare data security.
How Gateway.fm Simplifies Blockchain for Healthcare
Implementing blockchain in healthcare is often complex and resource-intensive. We remove these barriers by providing ready-to-use, enterprise-grade infrastructure that eliminates the need to build systems from scratch.
With us, launching a customized blockchain solution takes just a few clicks. We offer ready-to-deploy blueprints and modular components like indexers, oracles, account abstraction, identity solutions, and more. This enables secure, efficient, and compliant blockchain adoption, allowing healthcare organizations to focus on patient care instead of backend complexity.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain is not a cure-all, but it’s a powerful tool for solving some of healthcare’s most pressing challenges such as fragmented data, security risks, and process inefficiencies. It offers tangible benefits like cost reduction, faster operations, improved trust, and stronger compliance.
As the healthcare industry evolves, blockchain presents an opportunity to modernize systems and improve outcomes. A phased, thoughtful approach to adoption can help organizations enhance data management, streamline workflows, and build lasting trust with both patients and regulators, positioning them for the future of care.
Other blog posts
Want to read more? Discover our other articles below!



